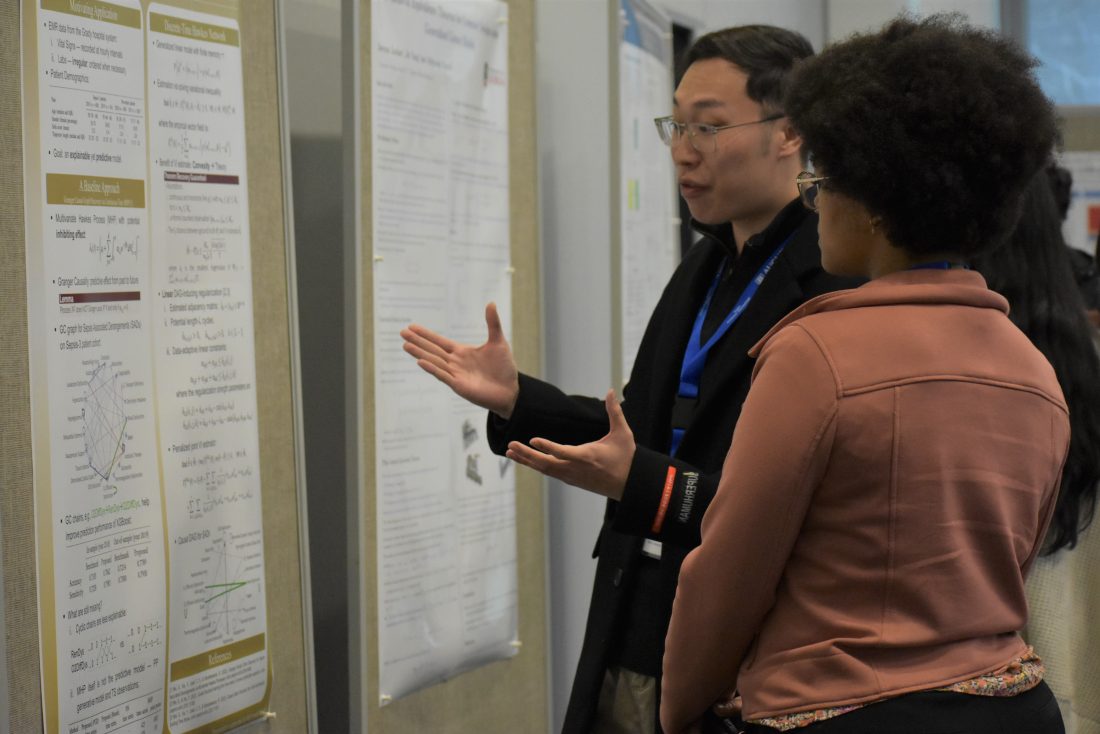
The Department of Population Health Sciences in the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University and the School of Computer and Cyber Sciences recently hosted a workshop titled “Emerging Data Science Methods for Complex Biomedical and Cyber Data.”
The goal of the March workshop was to promote collaborative research among those studying data science, statistics, cybersecurity and related disciplines to tackle the most challenging data- and model-driven scientific problems while equipping the next generation of the STEM workforce with the necessary skills.
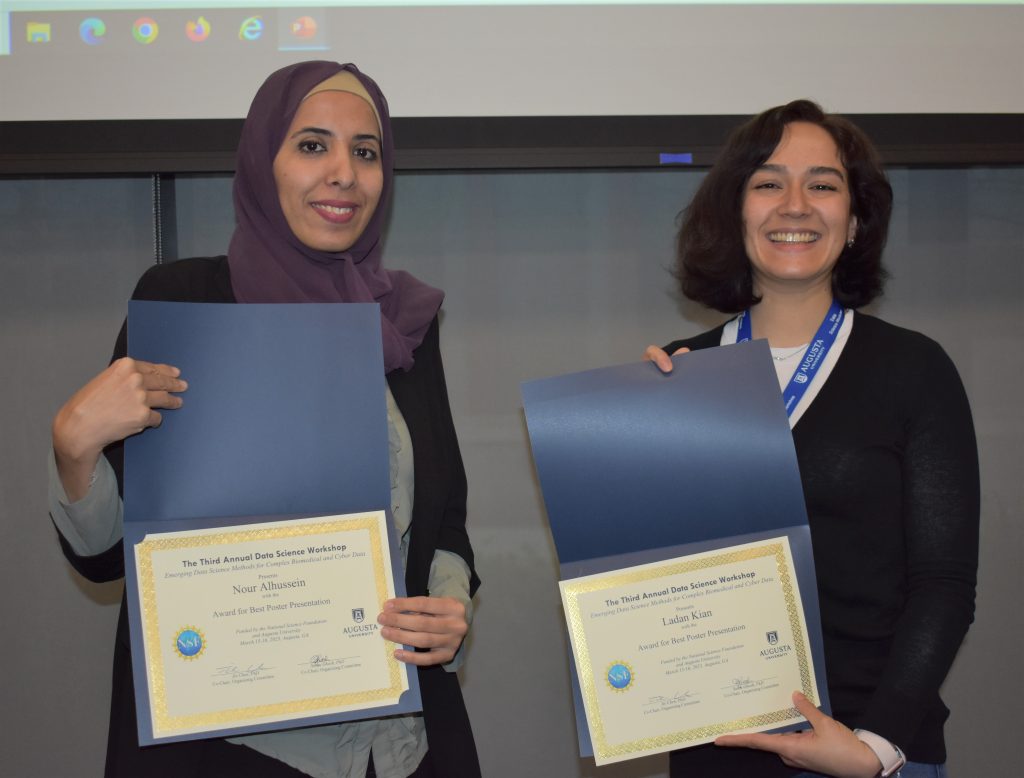

The explosion in the volume and complexity of data generated from various disciplines, social media, cyber traffic and the environment over the past decade has highlighted the need for collaboration among various disciplines.
“Each year we generate more data than in the entire prior history of humanity. Extracting information and knowledge from large amounts of data from various sources remains and will continue to be a most significant challenge,” said Alex Schwarzmann, PhD, dean of the School of Computer and Cyber Sciences. “Collaboration by data scientists and statisticians with domain experts from other disciplines can bring together their unique strengths in solving these challenges.”
Jie Chen, PhD, professor and division chief of Biostatistics and Data Science in the Department of Population Health Sciences, served as co-chair for the workshop.
“The goal of the two-day workshop is to educate and empower undergraduate and graduate students, postdoctoral fellows and early career researchers and faculty members with emerging statistical and computational methods to address the complex data arising from various fields of biomedical science and cyber science,” Chen said. “The workshop supports the needs of rural Georgia, outside of Atlanta, and nearby Southern states where such educational opportunity is scarce.”
Over the course of two days, leading experts from various institutions presented on topics ranging from statistical and data science methods for handling complex biomedical and cyber science data to lectures on ways to help participants develop analytical thinking, statistical reasoning, communication skills and creativity.
The event provided a unique opportunity for participants to share statistical and data science methods and learn statistical and analytical reasoning in various domains from leading experts in the field.
Sixteen institutions participated in the workshop, including Georgia State University, Georgia Tech, Johns Hopkins University, Medical College of South Carolina, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, University of Georgia, University of Louisville, UNC-Chapel Hill and Yale University
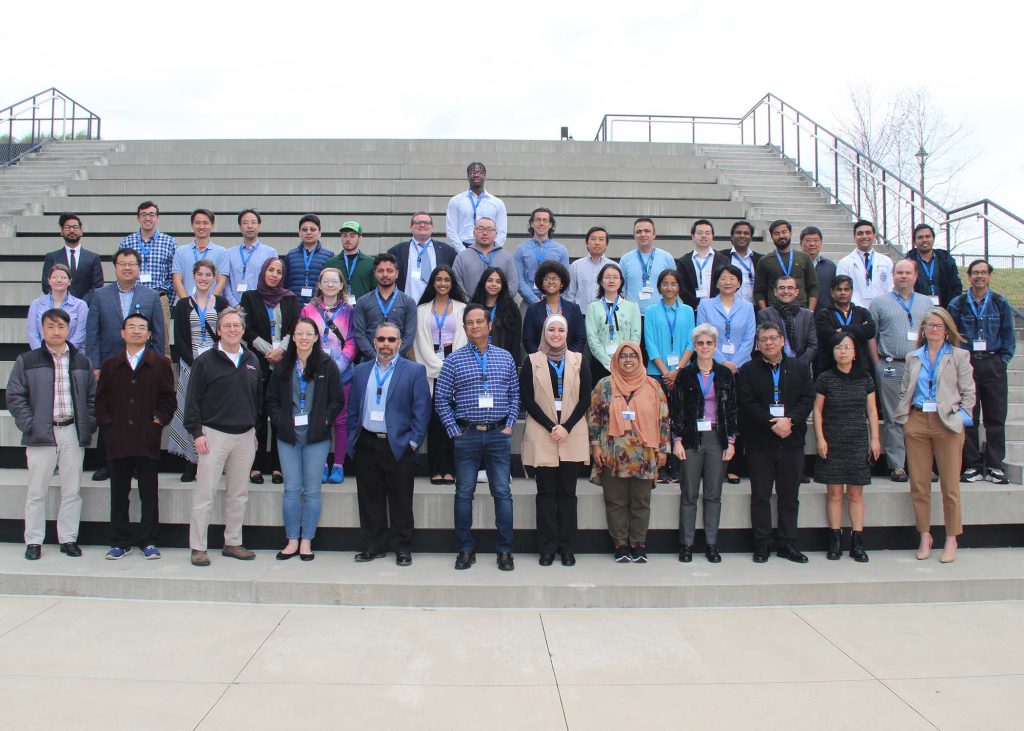

“This year’s workshop was very successful,” Chen said. “Workshop participants were exposed to emerging statistical and data science methods that may be utilized to solve problems facing the next generation of complex data. They learned state-of-the-art forefront data science research methods with the topics of deep learning, statistical machine learning, differential privacy on cyber data, Bayesian data integration, modeling of high-dimensional data and cybersecurity data modeling, used in real-world applications.”
This workshop was partly funded by the National Science Foundation through a grant award to Chen, principal investigator, and Santu Ghosh, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, co-principal investigator and senior vice president of research.
 Augusta University
Augusta University




